Difference between revisions of "Leather cutting"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[bild:LEATHER-DICTIONARY.jpg|300px]] | [[bild:LEATHER-DICTIONARY.jpg|300px]] | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Der Lederzuschnitt== | ||
| + | Whether [[car leather]], [[leather furniture|furniture]], [[leather clothing|clothing leather]] or for [[leather shoes|shoe leather]]: Leather has to be cut first, except it is used as complete skin. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 12: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Depending on the design, the cutting can be very complex.''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | + | Since a leather skin has a [[Parts of the hide|non-uniform outer contour]], there are [[Natural markings on leather|defects in the leather]] and not all areas of the skin are of the same [[leather quality|quality]] or have the same [[Leather grain - Grain side|grain pattern]], the art of cutting leather lies in the optimal area yield while taking all these aspects into consideration. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 25: | Line 24: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''A [[Parts of the hide|non-uniform outer contour]], [[Natural markings on leather|defects in the leather surface]] and [[Leather grain - Grain side|grain pattern differences]] must be considered.''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''[[ | + | ''[[Natural markings on leather]] are marked and spared during cutting.'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 203: | Line 202: | ||
== Additional information == | == Additional information == | ||
* [[Natural markings on leather]] | * [[Natural markings on leather]] | ||
| − | |||
* [[Leather defects]] | * [[Leather defects]] | ||
* [[Leather cutting waste]] | * [[Leather cutting waste]] | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 29 January 2017
Contents
Der Lederzuschnitt
Whether car leather, furniture, clothing leather or for shoe leather: Leather has to be cut first, except it is used as complete skin.
Depending on the design, the cutting can be very complex.
Since a leather skin has a non-uniform outer contour, there are defects in the leather and not all areas of the skin are of the same quality or have the same grain pattern, the art of cutting leather lies in the optimal area yield while taking all these aspects into consideration.
A non-uniform outer contour, defects in the leather surface and grain pattern differences must be considered.
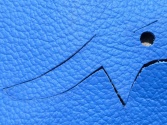
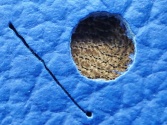
Natural markings on leather are marked and spared during cutting.
Ein Zuschneider muss daher die Haut beidseitig auf Fehlstellen prüfen. Das können Farbfehler oder Schäden in der Haut sein. Er muss bei gewünschtem gleichem Narbenbild die Schablonen so auslegen, dass die fertigen Objekte eine Narbengleichheit aufweisen. Dazu muss er für die Belastungsbereiche bei Möbel- oder Polsterledern die besseren Mittelbereiche auswählen. Dazu müssen die Schablonen so optimal ausgelegt werden, dass ein möglichst kleiner Verschnittrest übrig bleibt. Leder wird nach Fläche verkauft, und jede nicht genutzte Fläche erhöht die Kosten. Im Möbel- und Fahrzeugbereich liegt der Verschnitt i. d. R. zwischen 30 und 45%. Je größer die benötigten Zuschnitte sind und je kleiner die Häute sind, desto mehr Verschnitt fällt an.
Manche Hersteller weisen auf die Naturmerkmale des Leders hin und schneiden diese mit in den Zuschnitt rein, solange die Stabilität des Leders gewährleistet ist. In solchen Fällen reduziert sich der Verschnitt und der Konsument erhält auch kein schlechtes Leder. Der Kunde muss nur ausreichend informiert sein und solche Oberflächenunterschiede nicht als Mangel empfinden.
Beim Zuschneiden muss darauf geachtet werden, dass die Narbung möglichst gleich ist. Hier hängt es von der Kundeninformation ab, ob der Narbenunterschied akzeptabel ist.
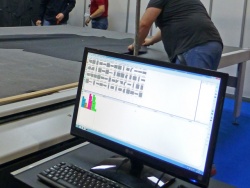
Die Zuschnittteile werden am Bildschirm ausgewählt und auf der eingescannten Haut um die markierten Schadstellen verteilt.
Weitere Informationen
Handzuschnitt
Bei Einzelanfertigungen oder geringen Stückzahlen kann der Zuschnitt mittels Schablone erfolgen. Eine Schablone wird aufs Leder aufgelegt und angezeichnet. Danach wird das Leder per Hand mit einer Schere oder einem Messer ausgeschnitten. Wichtig! Markierungen mit Permanentstiften auf Tintenbasis können abfärben und zu Abfärbungen führen. Es gibt verschiedenste Stifte zur Markierung von Leder, die keine Abfärbungen erzeugen.
Die Schnittlinien werden mit einem Silberstift vorgezeichnet und mit einem Spezialmesser (Kneip) geschnitten (Werkzeug erhältlich bei www.ledermanufaktur.com)
Markierungen der Silbermine müssen feucht abgewischt werden. Einfacher zu handhaben sind Peel-Off-Marker, die einfach mit dem Finger abgerubbelt werden, erhältlich bei www.lederzentrum.de
Machine cut
For cutting leather, there are various automated cutting machines. There is the possibility of detecting the external contours of the leather skins by laser. For this purpose, leather damages are marked. Computer programs then calculate the optimal cutting. The skin is then aligned on the cutting table. The outer contour of the previously scanned skin is marked on the table by light, so that the skin is correctly positioned. Then the skin is sucked to the table by vacuum and the cutting is automatically performed by a knife or water jet. When cutting with knives, small knives are used that cost less than 10 euros and cut up to 15 kilometers without interchange.
For soft or wavy leathers, a plastic film is placed over the outer edges of the skin. Due to the vacuum, the edges are fixed flat on the cutting table and can no longer lift contacting the cutting knife.
A foil prevents the leather edges from rising. - The cutting with a knife.
Even with knives you can cut very fine contours with the automatic cutting of leather.
After cutting, the blanks are optically marked with a laser so that the parts can be pre-sorted more easily for the next step. To simplify the work, the same parts are illuminated with the same color.
Laser lighting as working aid. - Leather cutting waste.
Cutting with the water jet is done with a 0.1 nozzle and strong pressure. Finer contours can be cut than with the knife. The leather is not significantly wet by cutting with water.
The automatic cutting with the knife has only problems with smallest detailed contours.
The automatic cutting with the water jet can cut detailed contours more precisely.
In the saddlery in Zuffenhausen at Porsche work approx. 250 employees. The car seats are cut exclusively with water jet cutting systems. For a Porsche 911 approx. 5 hides are processed.
With cheaper cut-to-size tables, it is possible to illuminate the postions on the cutting table and the leather is then positioned under the light, held in position by vacuum and then automatically cut.
Illuminated cut and finished cut, seen at www.ledermanufaktur.com).
Punching leather
Leather is also punched. The punch knives are then laid on the leather and then pressed into the leather with a punching press.
Punching tool for punching four leather symbols. - Different punching tools.
The swing arm punch machine for leather is often used. The punching is triggered on two handles so that the hands can not be injured under the press.
In order to punch as many parts as possible in one working step, several tools or tools with several fields can be laid on and leather can be superimposed several times. The highest yield is obtained with as many punching tools as possible and with a maximum of leather layers.
Cutting leather with a laser
Leather can also be cut with a laser. As with waterjet cutting, fine contours are no problem. However, since the laser is a combustion process, the leather smells accordingly and the soot of the cut edges is can cause stains. It is therefore always necessary to check whether punching or knife cutting or waterjet cutting is the better alternative.
With a laser-cut leather.
Additional information
- Natural markings on leather
- Leather defects
- Leather cutting waste
- Measures and weights
- Laser engraving - Laser cutting leather
- Hole punching









































 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution